307 words
2 minutes
[CS5446] Real World Planning & Acting
Heuristic Planning
to increase efficiency
- heuristic function : estimates the distance from state to goal
- find admissible heuristic estimations: doesn’t over / under estimation
- relaxed problem:
- add more edges: easier to find path to goal
- ignore precondition from action (all actions can be chosen at any state)
- e.g. 8-Puzzle
- remove the precondition
- now tiles can swap with any tiles, doesn’t have to be adjacent
- the heuristic estimate becomes # misplaced tiles
- e.g. 8-Puzzle
- ignore delete list (no reversing), assume goal states are all positive.
- goals are never undone
- e.g. 8-Puzzle
- each block will have more and more numbers.
- ignore precondition from action (all actions can be chosen at any state)
- state abstraction
- ignore some fluents
- solution in abstract state space will be shorter than in original space
- e.g. Air Cargo Transportation
Original problem:
- 10 airports, 50 planes, 200 cargos.
- Total # of states: (planes at airports) (cargos at airports or planes)
Relaxed problem:
- All cargos are in 5 airports, all cargos in same airport have same destination. => 5 big planes, 5 big cargos
- Total # of states:
- add more edges: easier to find path to goal
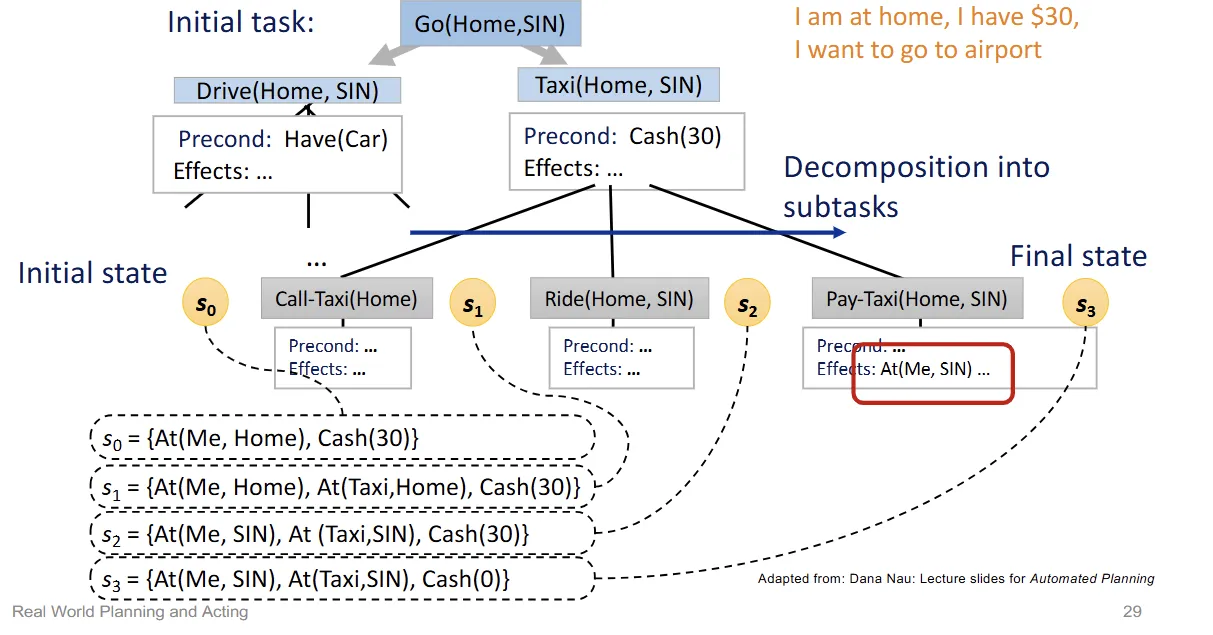
Hierarchical Planning
to manage complexity
- divide tasks into different subtasks
- Deferred (推遲) planning: plan details only after choosing that refinement
- Hierarchical task networks (HTNs)
- environment: Fully observable, deterministic
- High-Level Actions (HLAs)
- Each HLA has one or more refinements into a sequence of actions
- Refinements: can be an HLA or a primitive action
- HLA implementation: HLA refinement that contains only primitive actions
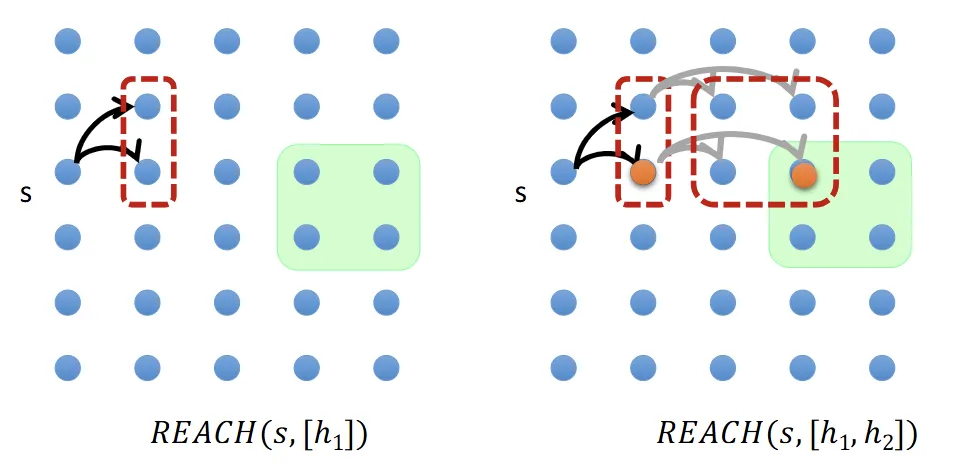
Searching for Abstract Solutions
Determine if reachable sets of a sequence of HLAs overlap with goals
Reachable set
- the set of states reachable by any of the HLA’s implementations
- Notation:
- means possibly
- e.g. means add / unchange.
- Approximation of effects
- Optimistic Reachable Set (): may overestimate the actual reachable set
- Pessimistic Reachable Set (): may underestimate the actual reachable set
- If optimistic set intersect with goal: may succeed
- If optimistic set doesn’t intersect with goal: must fail
- If pessimistic set intersect with goal: must succeed
- If pessimistic set doesn’t intersect with goal: must fail
- If not pessimistic set but optimistic set: uncertain, refinements needed
[CS5446] Real World Planning & Acting
https://itsjeremyhsieh.github.io/posts/cs5446-2-real-world-planning-and-acting/