255 words
1 minutes
[CS5242] Convolution Neural Networks (CNN)
Convolution
- Linear transformation
- Feature extraction
- 1D: Text, 2D: Image, 3D: microscopy …

Why convolution?
- Sparse connection: each output only connect to inputs in reception field
- fewer parameters, less overfitting
- Weight sharing (use the same kernel weight)
- regularization, less overfitting
- Location/ Spatial invariant
- same prediction for same input no matter where
1D Convolution
- : kernel/ filter (weights to be trained)
- : input
- : output feature
- applied area = receptive field: generate one output value

Padding
What to do with boundary cases?
- determine edge values
- we want all elements to be processed the same # of time
- we also want output size = input size
pad with extra values (0)
- without padding:
- with padding:
- => same padding:
Stride
How to make training faster?
- steps to skip
- consecutive: stride = 1
- : skip some elements
- faster, efficive
- same padding:
=>
2D Convolution

- Shape:
- input =
- kernal =
- output = =
- Computational cost:
- Multiple kernels: different levels of information (local vs. global)
- Multiple channels: results for all channels are summed (e.g RGB)
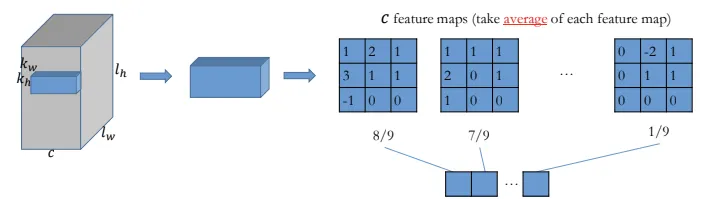
Pooling
What to do for reducing size?
- Aggregrate information from each receptive field
- average, maximum
- No parameter
- Applied for each channels respectively
- Reduces feature/ model size
- Invariant to rotation of input
- e.g Average pooling
[CS5242] Convolution Neural Networks (CNN)
https://itsjeremyhsieh.github.io/posts/cs5242-4-convolution-neural-networks/